5. Colour Vision and Visual Adaptation
Colour vision testing uses screening tests to find inherited colour vision defects among people with normal sight. All positive findings need to be assessed by using quantitative test, of which the Farnsworth Panel D-15 has become a standard test in routine examinations. Its variant Panel 16 has large colour surfaces for assessment of colour vision in visually impaired people and a thin layer of plastic covering the Munsell paper so that children's fingers would not ruin the colour surface. When the double set of the 16 caps is used, it is possible to start testing at the age of two years.

Video 1 & Video 2 & Video 3
The test instructions of the Panel 16 describe variations in test situations at different communication levels. The adult type testing is often possible at kindergarten level. When deaf children are tested, an older deaf child is often the best interpreter in explaining what the child is expected to do. The quick and efficient way of finding the correct colour caps demonstrates a normal colour perception in this deaf boy.
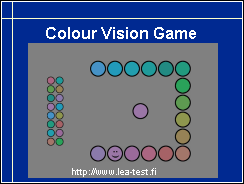
Colour Vision Game is a simple game to train children for the test situation and to have a preliminary diagnosis of the colour confusions that the child has.

Visual adaptation to higher luminance levels requires only a brief moment if the visual system is normal. In many visually impaired persons dazzle is the worst problem and absorptive and filter lenses often their most important low vision devices. Photophobia is usually diagnosed early and children receive absorptive lenses already during the first year.
Understanding changes in adaptation to lower luminance levels is rare although inherited retinal disorders like retinitis pigmentosa are common. Especially important is it to observe and investigate adaptation to mesopic luminance levels in all hearing impaired children because among them retinitis pigmentosa is common.
CONE Adaptation test was designed to detect delays in cone adaptation and thus also retinal dysfunction early. Delay in cone adaptation occurs often before school age when the changes in rod function are difficult to measure. The measurement requires only a few seconds and costs nearly nothing. Since it can be used by teachers and therapists at school, it is recommended as a screening test at the schools for deaf children.
Visual functions discussed so far can be measured and observed as a part of usual day care or classroom work to collect information on functional vision in play and school situations. As said before, the results may be better in day care than in the ophthalmologist's office. Values measured at a low vision centre may be better than those measured at school because the low vision therapist may have arranged the luminance level quite optimal, the ergonomic situation comfortable and may have been very supportive during testing. Measurement of visual field and motion perception are often the most difficult parts of assessment of vision.
